Somalia Crisis Recovery Project
Target: 1,850,207
Target: 885,875
Target: 1,236,583
The Somalia Crisis Recovery Project (SCRP), is a flood and disaster recovery, and reconstruction project financed by the World Bank via the Federal Ministry of Finance (MOF). Total Amount of the project is USD 187.5 M. It builds on responding the large number of recovery and resilience needs identified during FINA/DINA assessments and the subsequent National Recovery and Resilience Framework RRF. The project is aligned with the existing national policies such as NDP-9 and more specifically to the Recovery and Resilience Framework (RRF).
Key to SCRP's success is its central focus on an inclusive, government-led approach that fosters cooperation and coordination across federal and state government entities, while building trust with the public. This emphasis on collaboration is designed into the project's very architecture. The Office of the Prime Minister (OPM) chairs the Project Steering Committee (PSC) which provides strategic oversight. The Project Implementation Unit (PIU) acts as the implementing arm and is housed in the Ministry of Finance (MoF) and co-managed and staffed together with the Ministry of Planning, Investment, and Economic Development (MoPIED). State Project Teams work in step with the PIU in order to support implementation efforts in the FMS and create pathways between federal and state levels of government.
The project covers multiple sectors to provide a comprehensive, multi-phased mix of early recovery and medium-term reconstruction interventions, while also making long-term resilience building a key underpinning of all operations.

For those assets and services the Project rebuilds, it will do so focusing on making them stronger and more resilient to future disasters and climate shocks.

The Government has adopted all environmental and social safeguard requirements for the project so that activities can be implemented safely and without harm to the environment.
ransitioning external resources towards a greater emphasis on development will take time. By coordinating recovery and resilience-building investments through the SCRP, the FGS is building capacity as well as its ability to lead planning and coordination efforts. This being done across government and partners by establishing new technical working groups and collaborative work planning.
The project addresses the unique recovery needs of vulnerable populations through beneficiary targeting and consultation at the community level. This includes support to victims of Gender-Based Violence (GBV)/Sexual Exploitation and Abuse (SEA).

The FGS is directly engaging a select number of United Nations (UN) agencies and civil society consortia to support project implementation. This approach enables quick execution by leveraging partners' ability to immediately operate at scale, while also ensurin the government remains central to all decision-making and oversight.

Mogadishu(SONNA)-In a significant step towards building a more resilient Somalia, the Federal Government today convened a high-level Disaster Risk Finance…
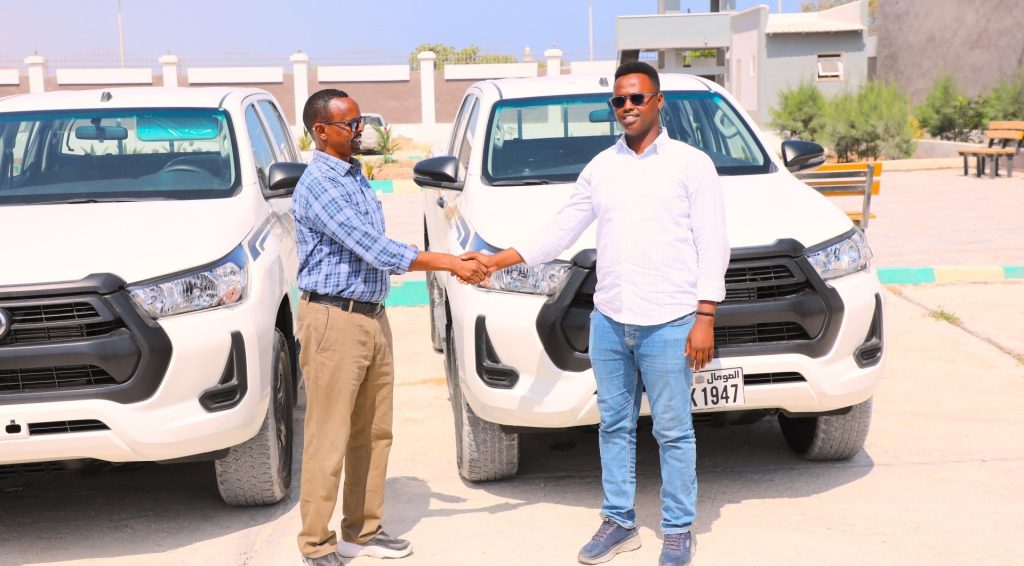

Mogadishu, Somalia – In a significant boost to its disaster response capabilities, the Somali National Disaster Management Agency (SoDMA) has…
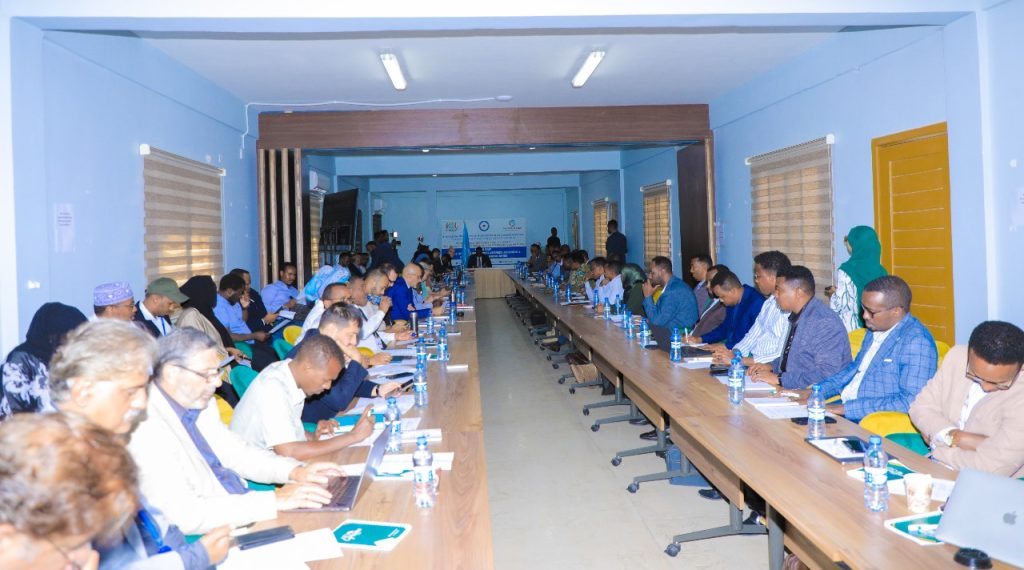

Mogadishu(SONNA)-In a significant step towards building a more resilient Somalia, the Federal Government today convened a high-level Disaster Risk Finance…









































